Last Updated on December 17, 2024 by Akhilesh

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare, transforming everything from diagnostics to personalized treatment plans. However, as AI takes a stronger foothold in healthcare, it raises significant concerns about security and privacy. Patient data, often the core fuel for AI-powered solutions, is highly sensitive. Mismanagement or breaches in this data could have catastrophic consequences not only for individuals but also for the healthcare system as a whole. In this blog, we’ll discuss some emerging security and privacy concerns associated with AI in healthcare, exploring the risks, regulatory challenges, and best practices for ensuring data protection.
The Role of AI in Healthcare
AI is playing an increasingly central role in modern healthcare. From AI-powered imaging systems to predictive analytics and robotic surgery, the technology promises to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and make healthcare more efficient. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, providing insights that would take humans far longer to gather.
- Diagnostics and Imaging: AI algorithms can interpret medical images, such as MRIs and CT scans, often with a higher degree of accuracy than human doctors. This leads to faster diagnoses and fewer errors.
- Personalized Medicine: AI can predict how individual patients will respond to specific treatments, enabling more tailored healthcare plans.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can identify at-risk patients, allowing healthcare providers to intervene early, preventing disease progression and reducing hospital admissions.
However, the benefits of AI are counterbalanced by concerns regarding the vast amounts of sensitive data required to train these systems.
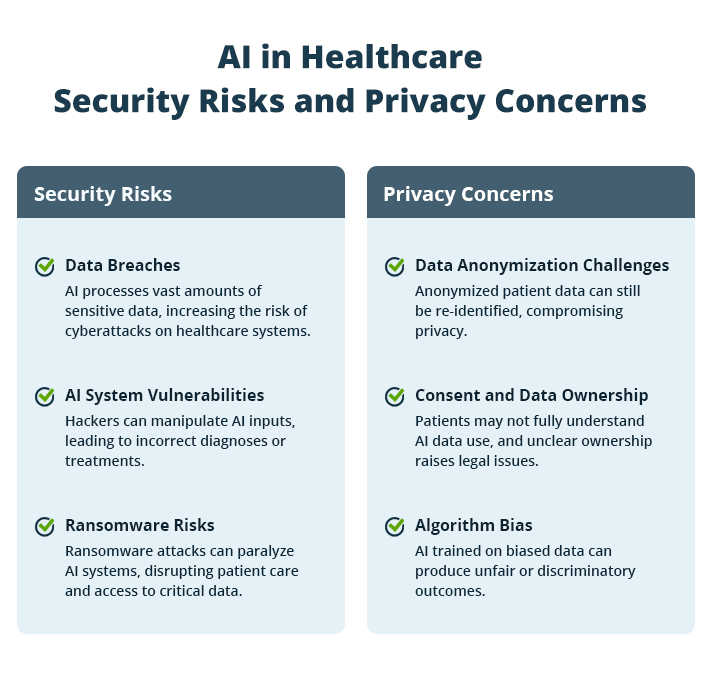
Security Risks Associated with AI in Healthcare
Healthcare data is a prime target for cybercriminals. The adoption of AI in healthcare has increased the volume and variety of data being generated, processed, and stored, making healthcare institutions even more attractive targets for cyberattacks.
1. Data Breaches
AI systems require massive amounts of patient data to function effectively. This data includes not only medical histories but also genetic information, lifestyle data, and even social factors that could affect health outcomes. The sheer volume of data increases the attack surface, making it easier for cybercriminals to infiltrate systems.
In 2021, a ransomware attack on Ireland’s Health Service Executive (HSE) led to the shutdown of hospital IT systems across the country, affecting patient care. Such breaches are costly, not only in terms of financial loss but also the trust that patients place in healthcare providers.
2. AI System Vulnerabilities
AI systems themselves can be vulnerable to attacks. Hackers could manipulate the data fed into AI algorithms, leading to incorrect diagnoses or treatment recommendations. These types of attacks are particularly concerning because they can go unnoticed for long periods, with severe consequences for patient health.
- Adversarial Attacks: In adversarial attacks, hackers subtly manipulate the input data to trick the AI into making errors. For example, an altered medical image could cause an AI system to miss a cancer diagnosis or misidentify a healthy individual as sick.
3. Ransomware and Data Encryption Risks
Ransomware attacks pose a severe risk to healthcare systems that rely on AI. In such attacks, hackers gain control over data by encrypting it and demanding a ransom to restore access. Given the essential role that data plays in AI, such attacks can cripple healthcare institutions, leading to delays in treatment and diagnosis.
Major Privacy Concerns in AI-Driven Healthcare
Privacy is another critical concern in the implementation of AI in healthcare. The collection, processing, and storage of sensitive patient data introduce several risks:
1. Data Anonymization Challenges
AI systems often require large datasets to train effectively, and healthcare providers typically attempt to anonymize patient data to protect privacy. However, research has shown that even anonymized data can be re-identified under certain circumstances, particularly when datasets are combined with other sources of information.
- Re-identification Risk: A 2019 study showed that AI could re-identify 99.98% of individuals in anonymized datasets using only 15 demographic attributes. This puts patient privacy at risk, even when data is anonymized.
2. Consent and Data Ownership
AI-driven healthcare often involves data sharing between multiple organizations, including hospitals, research institutions, and tech companies. This raises questions about patient consent and data ownership.
- Informed Consent: Patients may not fully understand how their data is being used by AI systems, making it difficult for them to give truly informed consent.
- Data Ownership: When third parties, such as AI developers, gain access to patient data, it becomes unclear who owns that data. Does it belong to the patient, the healthcare provider, or the AI company? This lack of clarity can lead to legal disputes and ethical dilemmas.
3. Bias in AI Algorithms
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data is biased, the AI will be biased too. In healthcare, this can have serious implications, particularly for marginalized groups.
In a widely cited 2019 study, researchers found that an AI algorithm used to guide healthcare decisions systematically favored white patients over Black patients when allocating healthcare resources. This occurred because the system used historical healthcare spending as a proxy for health needs, which overlooked the systemic biases that had previously disadvantaged Black patients.
Download Whitepaper

Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
Given the sensitive nature of healthcare data, regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in ensuring that AI is deployed safely and ethically. However, existing regulations struggle to keep up with the rapid pace of AI development.
HIPAA and GDPR
In the U.S., the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) governs how patient data is used, stored, and shared. In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) provides similar protections. Both regulations focus on data privacy and security, but neither was designed with AI in mind.
- Challenges: HIPAA and GDPR primarily focus on protecting identifiable patient information, but AI systems often rely on vast amounts of anonymized data, which these regulations do not always cover. Additionally, neither regulation fully addresses the ethical concerns around AI’s decision-making processes, such as how to ensure transparency and accountability in AI-driven healthcare decisions.
AI-Specific Guidelines
Some countries are beginning to introduce AI-specific guidelines for healthcare. For instance, the European Union has proposed the AI Act, which aims to regulate high-risk AI applications, including those in healthcare. These guidelines focus on ensuring that AI systems are transparent, traceable, and accountable.
- The Need for Global Standards: The AI Act is a step in the right direction, but a global standard is needed to ensure that AI systems in healthcare are held to the same ethical and security standards across borders. This would help to prevent companies from operating in regulatory gray areas and ensure consistent protection for patients.
Best Practices for Securing AI in Healthcare
While the challenges are significant, there are several best practices that healthcare providers, AI developers, and regulators can adopt to mitigate security and privacy risks.
Data Encryption and Secure Storage
Healthcare providers should ensure that all data, especially sensitive patient information, is encrypted both at rest and in transit. Encryption makes it significantly harder for cybercriminals to access or tamper with data.
Regular Security Audits
AI systems should be subject to regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities. This should include not only the systems themselves but also the data they rely on, ensuring that any potential breaches are caught and mitigated before they can do harm.
Ethical AI Development
AI developers should prioritize ethical development, ensuring that AI systems are transparent, explainable, and free from bias. This involves careful consideration of the data used to train AI systems and constant monitoring to ensure that they do not perpetuate existing inequalities.
Stronger Regulatory Oversight
Regulatory bodies must stay ahead of the curve by updating existing laws to account for the unique challenges posed by AI in healthcare. This could involve the introduction of AI-specific regulations or amendments to existing frameworks like HIPAA and GDPR to include provisions for anonymized data and AI-driven decision-making processes.
Conclusion
While AI holds incredible promise to transform healthcare, it also brings serious security and privacy challenges. To fully realize the benefits of AI, healthcare providers, tech developers, and regulators need to come together, safeguarding patient data and addressing the ethical issues that come with it. This involves not only implementing strong security measures but also creating transparent, accountable AI systems that can be trusted to make fair, unbiased decisions. With the right safeguards in place, AI can truly transform healthcare for the better, improving patient outcomes while protecting privacy and security.

 Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration
Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration 15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them
15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them Why the AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
Why the AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
