Last Updated on January 17, 2025 by Deepanshu Sharma

At 8:00 a.m. on a Monday morning, the IT team of a mid-sized company noticed something unusual: employees were unable to access shared files, and strange filenames had replaced critical medical records. Moments later, a message appeared on every screen, demanding a hefty ransom in exchange for a decryption key to unlock the company’s data. In an instant, employees’ workstations were locked, sensitive information was at risk, and the entire business ground to a halt. This wasn’t an IT glitch, it was a ransomware attack.
Despite having firewalls and antivirus programs in place, the company was unprepared for this kind of attack. Panic set in as they scrambled to understand the extent of the damage and how to recover. This scenario plays out across industries every day, and it leaves many asking the same question: What do we do now?
Recovering from a ransomware attack requires more than just technical expertise, it demands a strategic, well-prepared recovery plan that can restore data, minimize damage, and get operations back on track. In this blog, we’ll cover the steps necessary to bounce back from a ransomware attack, from crafting a resilient data recovery plan to restoring encrypted files. Let’s dive in.
What is a Ransomware Attack?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software designed to encrypt a victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Attackers typically demand payment in cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, because it offers anonymity. Ransomware attacks can be devastating, leading to prolonged downtime, loss of sensitive data, and reputational damage. Businesses of all sizes, as well as individuals, can fall prey to these attacks.
Types of Ransomware
Ransomware comes in several forms, with the two most common types being:
- Crypto Ransomware: This form encrypts your data, making files unreadable without the decryption key. Attackers offer the key in exchange for a ransom.
- Locker Ransomware: Rather than encrypting files, locker ransomware locks users out of their devices or critical applications. While files remain intact, access is blocked until the ransom is paid.
Ransomware Data Recovery Plan
A ransomware attack can cripple your organization if you don’t have a solid data recovery plan in place. Having a well-thought-out plan ensures that you can quickly recover your data and resume operations without paying the ransom.
Key Components of a Data Recovery Plan
- Regular Backups
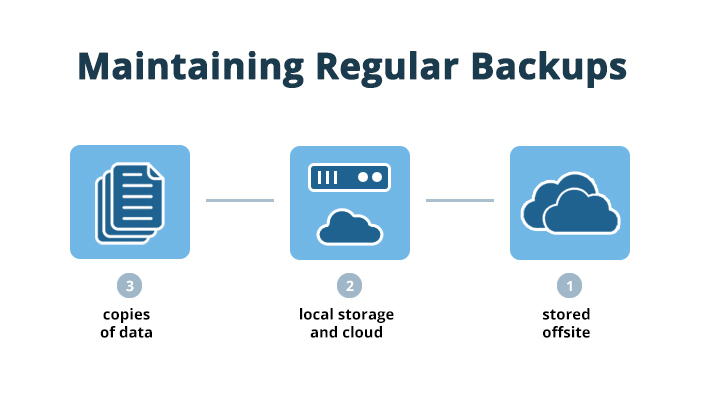
One of the most critical aspects of a recovery plan is maintaining regular backups. Follow the 3-2-1 rule:
- Keep 3 copies of your data.
- Store them on 2 different media types (e.g., local storage and cloud).
- Ensure that 1 copy is stored offsite or in an air-gapped environment (disconnected from the network).
2.Testing Your Recovery Plan
A plan is only as effective as its execution. Schedule regular tests of your backup and recovery systems. This includes mock drills and simulations to ensure that everyone in your organization knows their role and that the backup system functions as expected under real-time conditions.
- Cloud Backups
Cloud-based backups offer scalability and redundancy. Services such as Amazon S3 or Azure offer automatic backups with high security. However, it’s essential to ensure that these backups are also protected from ransomware by using immutable storage, which prevents any modifications to the backup data for a set period.
3. Employee Training
A recovery plan isn’t just technical—it involves people. Educate your employees about cybersecurity best practices, including phishing prevention and safe file-sharing techniques. Human error is one of the leading causes of successful ransomware attacks, so investing in training can mitigate this risk.
10 Steps to Recover from a Ransomware Attack
In the event that one, or several, of your company machines has become infected, what is the best course of immediate action to take? The following checklist walks you through the measures that should be taken once ransomware hits:
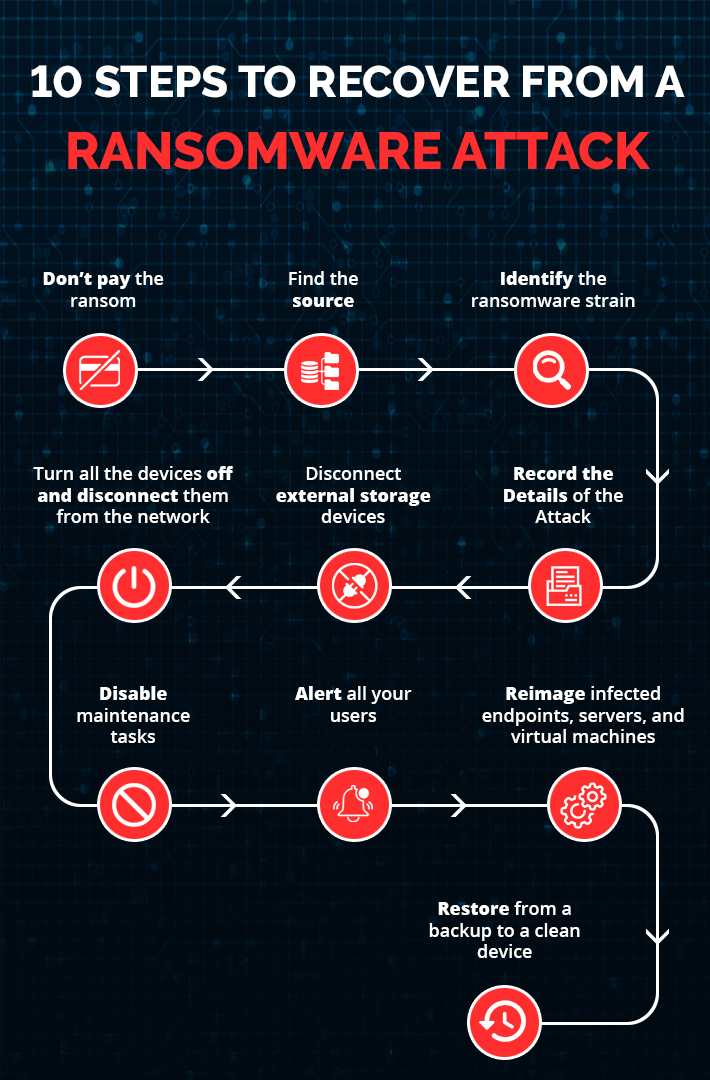
1. Don’t pay the ransom
While paying the ransom may seem to be the quickest way to get your data back and get on with your life, there is no guarantee that the person on the other end will unlock your files once they’re paid off.
2. Find the source
Now that you have taken steps to contain the immediate known damage, examine your IT environment for indications as to the source of the attack. Any system which is out-of-date is easily compromised, and it’s crucial to remember that even SaaS apps like Microsoft 365 are vulnerable. Reach out to all of your users to ascertain who experienced the first signs of the attack and when this occurred. Was it after they clicked on a link in an email? Or was there an unusual prompt coming from a web browser?
3. Identify the ransomware strain
Identifying the strain of ransomware can help to identify the encryption code you need to unlock your device. Decryption websites can provide you with decryption codes, so you can resolve the issue without paying a ransom. Knowing the strain of ransomware is also helpful to have when you go to the authorities to report the breach.
4. Record the Details of the Attack
Photograph the ransom note that appears on your screen which can be simply done using your phone. This will not only contain the details of how you are to pay the ransom, which is NOT recommended, but also can help recovery teams determine what ransomware hit you. This information is also helpful should you need to fill out any reports for police or insurance companies.
5. Disconnect external storage devices
It is crucial to keep backups of your files and these can be stored in the cloud or on external storage devices. The problem with many forms of malware is that it will also try to corrupt your external storage devices, making recovery efforts ineffective. Immediately remove external storage devices in the event of a ransomware attack to ensure they remain clean.
6. Turn all the devices off and disconnect them from the network
Once you’ve identified the devices that are infected, immediately disconnect the network cable, turn off the Wi-Fi, and shut those devices down. Many types of ransomware can spread via a network connection, so the sooner the infected devices are disconnected, the better your chances are of containing the breach.
It’s also essential to take all shared drives offline temporarily until you have determined that all the infected systems have been identified. At this stage, you should continue to monitor systems to see whether new files are becoming encrypted or disappearing.
7. Disable maintenance tasks
Many maintenance tasks on your device will continue to run as scheduled, regardless of a ransomware attack. Tasks like automatically emptying your Recycle Bin, cleaning out conversations, and deleting old files should be put on hold until the ransomware issue is resolved. Something could be deleted that you later need to eliminate the malware or direct authorities toward the source.
8. Alert all your users
Sending an email announcement and posting warnings on a company message board, to alert users of a ransomware attack is a good strategy but this is not sufficient in the event of a ransomware attack. You’ll need to physically go and speak with everyone directly to ensure that they’re all aware of what has happened and what they need to look out for.
9. Reimage infected endpoints, servers, and virtual machines
Once an environment has been infected, the only way to guarantee that the ransomware has been completely removed is to wipe all devices, including virtual machines clean, and start with a new image. In the meantime, your organization can continue to run if you have a cloud disaster recovery plan in place, allowing critical applications and data in virtual machines to be recovered in a virtual private cloud.
10. Restore from a backup to a clean device
After the damage has been contained, ensure that all users are aware of the current threat so that they will not cause further infection. Data can be recovered, without paying the ransom, by restoring it from a backup stored with a reliable cloud service such as AWS. With an enterprise-grade automated backup solution and knowing when and where the attack took place, you can immediately go back to an uninfected, indexed snapshot of each system’s data.
How Lepide Can Help
Lepide Data Security Platform offers a comprehensive solution for ransomware protection, helping you detect, prevent, and recover from attacks.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Lepide monitors for suspicious behavior like mass file modifications or unusual access patterns, raising instant alerts to help you act quickly.
- Automated Response Mechanisms: Automate responses to threats, such as disabling accounts or isolating infected systems, to minimize damage and limit attack scope.
- File Activity Monitoring: Track and log all file changes, including encryption and deletion, to spot potential threats early and gain insights into data access.
- Audit and Compliance Reporting: Generate detailed audit reports to track user behavior and access history, aiding in recovery and compliance after an attack.
- Backup and Recovery Support: Integrate with backup systems for swift recovery, restoring clean versions of infected files to minimize downtime and data loss.
- Insider Threat Protection: Monitor privileged user activity and access changes to detect and neutralize internal threats that could facilitate ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
Facing a ransomware attack is a harrowing experience that can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and strain resources. However, with a well-prepared recovery plan, the right tools, and strategic actions, organizations can navigate the aftermath with resilience and confidence. By implementing robust backup strategies, utilizing decryption tools, and seeking professional help when needed, businesses can recover from the grips of ransomware without falling into the trap of paying the ransom.
Moreover, strengthening your cybersecurity posture post-attack is crucial. Enhancing security measures, educating employees, and leveraging solutions like Lepide can significantly bolster your defenses and prevent future incidents. The path to recovery is challenging, but with a proactive approach and the right resources, your organization can emerge stronger and more secure.
Remember, preparedness is key. Investing in comprehensive data recovery plans and robust security measures today can safeguard your business against the uncertainties of tomorrow. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and keep your defenses strong.
If you want to know how Lepide can help you protect your organization from Ransomware attacks, schedule a demo with one of our engineers today.


 Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration
Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration 15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them
15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them Why AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
Why AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
