Last Updated on December 17, 2024 by Akhilesh

All organizations are powered by data. It supports corporate operations and stimulates creativity and decision-making. The fact that the data is often dispersed over several cloud and on-premises platforms makes it a nightmare to secure. As a result, the conventional methods of data protection have become outdated. This gave rise to a new strategy known as the data-centric approach.
What is Data-Centric Security?
Data-centric security is an all-encompassing strategy that protects sensitive data by concentrating on the data rather than the network or infrastructure. Its main goal is to safeguard the data at every stage of its lifespan, ensuring that it is safe even if security settings are violated.
Technologies, regulations, and procedures that are data-centric focus exclusively on securing the data itself. The concept is straightforward: instead of building stronger perimeters, such as more robust firewalls, while leaving the data vulnerable, the emphasis shifts to directly protecting the data. This ensures its security, regardless of the strength of external defenses.
Key Components of Data-Centric Security
The five essential components of data-centric security that we shall cover are listed below:
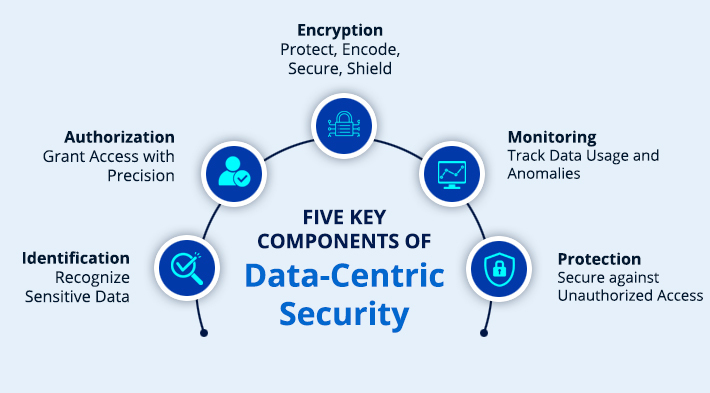
- Identification and Classification: Regarding security, data classification is classifying and labeling the data according to its attributes and giving each piece of data the right amount of protection and access. Identifying and classifying data based on its degree of sensitivity is the first step. Resources can be distributed and security protocols can be followed by identifying the most important data.
- Authorization: To guarantee that only authorized persons have access to sensitive information, access restrictions are implemented. Numerous authentication and authorization techniques, including passwords, multi-factor authentication, role-based access controls, attribute-based access controls, and more, can be used to confirm access controls. Fine-grained access controls and role-based permissions are crucial to limiting data access to approved individuals and roles and lowering the risk of data exposure.
- Encryption: Data is protected from unwanted access via encryption, ensuring that only people with permission can read and comprehend it. Data can be encrypted while it is in transit or while it is being stored in a single location (at rest). Encrypting data while it’s in transit and at rest provides an additional degree of security by preventing unwanted users from accessing it.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Data monitoring and auditing systems are employed to identify and address any security events or breaches. This may entail tracking data access, location, and lifetime, among other things. Potential security incidents can be promptly addressed with real-time activity monitoring and auditing tools that assist in identifying odd data access or transfer patterns.
- Remediation: In order to quickly identify the problem and minimize any harm, effective incident response is essential in the event of a breach or unauthorized access.
Need for Data-Centric Security
The amount of data required for daily operations has grown significantly. Three key factors make adopting a data-centric approach to data protection essential:
Security Measure
The shift to data-centric security has been largely influenced by the increase in data breaches and cyberattacks that target the data itself. With the advancement of hacking techniques, organizations have had to adapt their security procedures to better protect critical data. Data-centric security is a successful strategy for protecting an organization’s data from online threats. It might be integrated into the existing infrastructure without requiring large changes or causing major interruptions. As a result, organizations can further improve their security protocols and free up resources for other purposes.
Data-Centric Approach
Data-centric security is one of the most crucial methods for protecting dynamic data. More control over how your systems and networks are maintained is possible with fine-grained access controls, which are more effective than traditional access limits. This structure is important since not every user should have access to every piece of data in their department.
Hybrid Work Environment
The growth of remote work, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has also aided in the transition to a data-centric strategy. Securing data at the network or system level is getting harder as more and more data is exchanged across many devices and stored in the cloud.
Compliance Constraint
By putting in place suitable security controls and policies to safeguard sensitive data, data-centric security assists enterprises in adhering to data privacy laws. There are stringent laws governing data protection in several businesses. Organizations may comply with these regulations and avoid trouble by taking a data-centric approach.
Why Data-Centric Security is Required
Organizations have raised their cybersecurity spending as data becomes a more significant competitive advantage. The following list highlights the various advantages of investing in data-centric security procedures.
- Low Cost: In the end, data-centric security lowers the possibility of expensive data breaches by concentrating on the data itself. Numerous publications emphasize that attackers target data above all else and that the cost of a data breach rises every year. Additionally, it helps reduce the expense of maintaining compliance, which frequently calls for modernizing systems, equipment, and the technology that underpins them.
- Better Security Controls: Infrastructure is no longer the only aspect of ensuring data security. Securing individual files is becoming more important as security becomes more data-centric. This method makes it possible to track, store, and protect data more effectively. Additionally, file-level security makes it possible to put strong encryption methods into place in addition to strict access controls and policy enforcement. It is simpler to regulate user access to resources and restrict what and when they can use them when document security is given top priority.
- Establish Data Security: Organizations can avoid relying on any one system or device by implementing data-centric security measures. Especially with their supply chains, businesses can develop robust cybersecurity procedures that offer flexibility in data management instead of depending on a certain platform. This is important because, even though security infrastructure can make a system stronger, it can also make security the objective rather than the method of safeguarding an organization’s important data. Furthermore, in the case of a systemic failure, data-centric solutions minimize harm and the risks associated with data gaps.
Creating a Data-Centric Security Model
Data must be enclosed in successive layers of protection using a defense-in-depth approach to create a true data-centric security framework. Appropriate redundancies are provided by defense-in-depth to serve as barriers with progressively more complicated security layers.
- Data Discovery and Classification: The first step in creating a thorough data-centric model is to discover the data in your company’s ecosystem. Prior to putting in place any security measures, you must understand where your data is kept and how it is stored. Next, properly categorize this data to determine its worth and rank the degree of protection it merits. Then, security managers can implement precise safeguards for every type of information.
- Identity and Access Management(IAM): Strong data-centric security is mostly dependent on Identity and Access Management. Only authorized users have access to sensitive data in line with the least privilege concept. This guarantees that strong IAM procedures are in place to give efficient controls to prevent any unwanted access to private data.
- Data Governance: Adherence to industry-specific and governmental standards, including national and international obligations like GDPR or HIPAA, is essential for data-centric security to be really effective. For enterprises to stay in compliance with these requirements, data governance is essential, and risk assessments must be carried out on a regular basis.
- Data Loss Prevention(DLP): Integration of a data loss prevention solution that satisfies their business requirements for data protection is one of the greatest approaches to data-centric security. Through the detection and prevention of data compromise from beaches, leaks, and exfiltration, DLP excels at keeping data out of the wrong hands or from being subject to unauthorized access.
How Does Lepide Help?
Lepide Data Security Platform allows you to manage data security policies regardless of where the data is stored. Furthermore, it provides security teams with total insight into how their data is used and accessed across the whole company. Across many IT contexts, our technology offers a thorough insight into who accesses data, when, and how. Lepide facilitates the proactive detection of unwanted activity and access irregularities by utilizing real-time monitoring and advanced analytics. By automating processes like access control, classification, and data discovery, it guarantees adherence to data laws. Lepide assists businesses with risk mitigation, sensitive data protection, and decision-making by tracking user activity and producing informative insights.
Interested in investing in Data-Centric Security solutions to protect sensitive data? Set up a demo with one of our engineers.


 Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration
Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration 15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them
15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them Why AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
Why AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
