
Endpoint device sprawl continues to make data security more challenging for IT teams. Employees may be using a wide variety of devices, such as laptops, smartphones, or tablets, as well as their desktops, workstations and servers. Such endpoints are connected to confidential information and essential applications and services, which is what makes them such an appealing prospect for cyber criminals. Getting visibility and control over these endpoints presents a real challenge for any IT or security team. This is where Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions come into play.
What is Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)?
In a nutshell, EDR refers to cybersecurity software specifically aimed at comprehensive and ongoing endpoint monitoring with the capacity to detect and prevent suspicious actions. While the traditional antivirus works on the basis of identifying known threats, on the other hand, EDR operates on a different plane. It observes behavior patterns, gathers endpoint information and applies sophisticated statistical methods to discover trends that may indicate a cyber attack.
Today, the number of endpoints is significantly larger due to the increase in telework and the use of personal devices in the workplace (BYOD). EDR solutions serve to fill that gap by offering insights and response capabilities regarding such endpoints. However, what EDR means is important to understand for why this line of thinking is so popular in the contemporary approaches to cybersecurity? Let’s dive deeper.
What is the Role of EDR in Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity threats are no longer a question of whether it will happen, but rather when it will occur. The kinds of attacks being currently deployed are becoming more complex in nature, and hence while traditional measures such as firewalls or standalone antivirus solutions can be effective in detecting conventional threats, they become ineffective against more evolved ones. EDR has now evolved to be part of contemporary Cybersecurity doctrines because of the above gaps it fills.
Here’s why EDR is important:
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Unlike simple or regular full-spectrum scans, EDR solutions provide real-time analysis of endpoint activities to provide threat detection in real time.
- Proactive Response: The primary function that sets an EDR different from a simple threat detection solution is that EDR tools offer mechanisms for threat counteraction at the moment when the threat is identified, thus minimizing the possible threat impact.
- Increased Visibility: EDR provides a single point for visibility into endpoint activities and their trends and risks within an organization.
- Combating Advanced Threats: The nature of EDR enables it to identify threats missed by conventional solutions such as zero-day attacks and fileless malware, which are attributed to their behavior.
- Compliance and Risk Management: In the case of industries that involve the handling of sensitive data such as finance and health, EDR assists organizations to meet regulatory standards through effective endpoint protection.
Endpoints are gradually thought of as the biggest vulnerability to cyber security. EDR helps to guarantee that even if the hacker breaks through the perimeter, he does not have full access to your networks.
How Does EDR Work?
While the concept of EDR may seem complex, its functionality is straightforward when broken down:
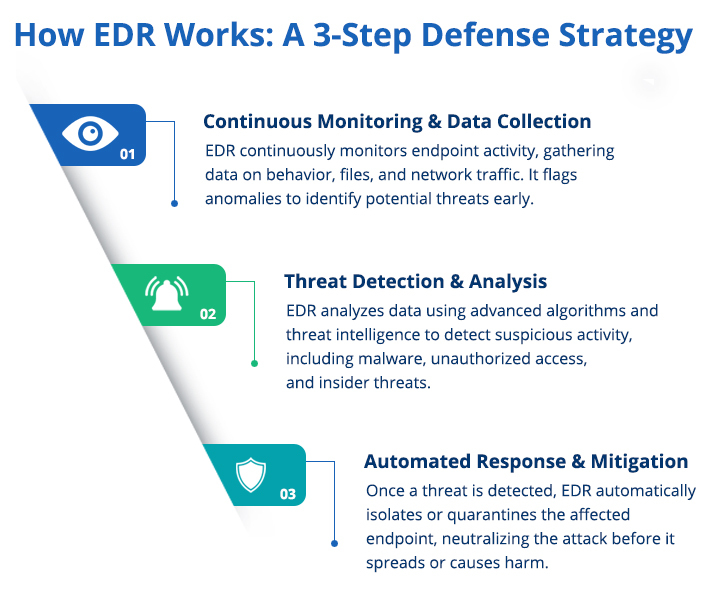
- Data Collection: EDR solutions are always passive and gather data from endpoints that may cover activity on files, network connections, applications and systems logs. Threat detection is based on this raw data.
- Threat Detection: Once data is collected EDR relies on signatures, behavioral analysis as well as machine learning algorithms to detect malicious activities. For instance, whenever an endpoint is suddenly communicating with an unknown IP address, or running scripts that are unauthorized, then the system considers the endpoint to be a threat.
- Investigation: EDR tools offer further information and attributes relating to activities that have been marked, including the source and the manner of the threat’s dissemination as well as the affected endpoints. TThis means that security teams are able to gain insight on the magnitude of the problem or situation.
- Response and Containment: If a threat is identified, the EDR system allows the security team to respond in real-time through methods like disconnecting the infected endpoint, terminating specific processes, or reverting any system alterations.
- Continuous Learning: Modern EDR solutions evolve through time basing on previous events, tweaking the mathematical algorithms that analyze the data in an attempt to classify new threats within the environment.
This cycle of detection, investigation, and response helps to ensure that threats are caught and neutralized as quickly as possible to reduce their impact and inconvenience.
What are the Capabilities of EDR?
Modern EDR solutions are expected to present an efficient scheme for protection against threats. At its basic level, it integrates detection, containment, investigation, and elimination methods to enable organizations approach endpoint security predictively. Here’s a closer look at these essential features:
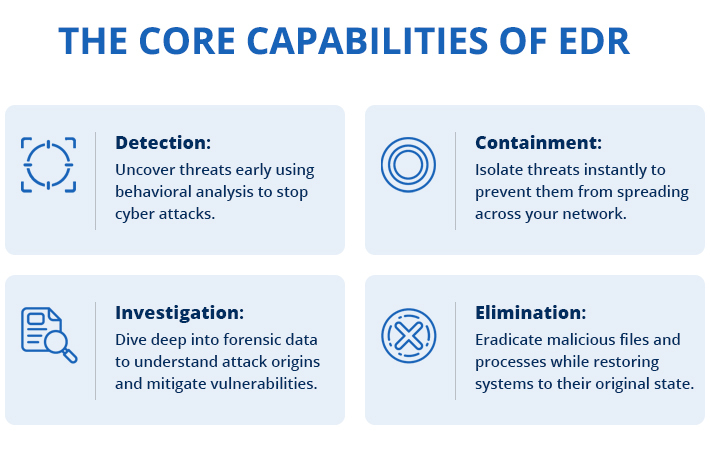
1. Detection
EDR solutions are always checking the endpoint activity and sometimes the activities are suspicious in nature. With the help of statistics and machine learning, and threat intelligence, known and unknown threats are determined. EDR, unlike conventional security solutions, does not use signatures to detect malware, but uses behavioral analysis to identify fileless malware or cyber threats. This makes sure that threats are detected early, most of the time before serious harm might happen.
2. Containment
In case of a perceived threat, EDR solutions offer the capacity to contain a threat before it spreads throughout a network. For instance, if malicious software is detected at a workstation, the EDR system can separate that particular endpoint from the entire network to entirely halt the attack. The practice of containment is useful in reducing the extent of harm during an incident is ongoing and provides security teams with mere time to act adequately.
3. Investigation
EDR platforms provide the security teams with a capability of responding to incidents through providing tools that can be used to investigate the incidents. While the EDR systems offer all the features of a standard antivirus product, they also allow for more detailed endpoint data gathering, including system logs, network connections and files that are changed by a threat. This is beneficial to security teams as it helps in finding the attack source, comprehending the spread or attack’s range and analyzing how the attackers got into the network. Such forensic data is crucial in identifying how the breach was realized and also in strengthening the boundaries against future threats.
4. Elimination
As soon as threat is comprehensively analyzed, EDR solutions provide an opportunity to eliminate it from the environment. This means stopping the execution of malicious processes that may compromise the system more, removal of the infected files, and reversing any modifications that may have been made by the attacker. Advanced EDR also provide the client with rollback capabilities that restores the systems used by the attackers back to their original state. EDR makes it easier to get rid of threats and minimizes the time taken to restore operations, while denying the attackers a chance to reconnect again.
Detection, containment, investigation, and elimination capabilities come together to provide an efficient protection against various endpoint threats. They not only reduce exposures to threats and risks in the current world but also give definitive results to organizations that will help to shore up their cybersecurity status.
10 Things to Consider While Buying an EDR Solution
Choosing the proper Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is an important decision that can make a big difference in the protection of the company. EDR tools are not all the same and it is therefore necessary to measure them against certain parameters that are most relevant to your enterprise and security strategy. Here are the key factors to consider when buying an EDR solution:
1. Comprehensive Endpoint Coverage
Your EDR solution should guard all forms of endpoints present in your organization, be it desktops, laptops, servers, or mobile gadgets. It should also fit well on various operating systems including Windows, macOS, and Linux for none of the endpoints remain at risk.
2. Real-Time Threat Detection and Response
Time is an essential factor in the fight against cybersecurity threats. Find an EDR solution that provides features like real-time monitoring, threat detection, and respond with automation. It makes a significant difference to be able to quickly cut off infected devices or kill specific processes to stop the attacker from moving around and doing more damage.
3. Behavioral Analysis and Advanced Threat Detection
Modern attacks often bypass traditional signature-based detection methods. Ensure the EDR solution uses behavioral analysis, machine learning, and AI to detect anomalies and unknown threats, such as zero-day vulnerabilities and fileless malware.
4. Incident Investigation and Forensic Capabilities
The EDR tool should offer specific information about events, such as factors contributing to the threat, impacted hosts, and threat paths. Forensic skills make it easy for your security personnel to determine how a breach happened and how best to avoid such outcomes in the future.
5. Automation and Customization
Manual investigation and response can be time-consuming and error-prone. Opt for a solution with automated workflows for detecting, analyzing, and responding to threats. Additionally, the ability to customize policies and configurations ensures the solution aligns with your unique operational needs.
6. Threat Hunting Tools
EDR tools should provide your security team with tools that will help in active hunting for threats proactively. This is because it enables the analysts to detect latent threats or emerging threats before reach full-blown attack.
7. Integration with Existing Security Tools
EDR tool is not sufficient enough if used alone. It must fit well into your existing security landscape such as; Firewall, Vulnerability management systems, etc. This helps in integration of these applications where they work collectively for better handling of your organization’s security needs.
8. Scalability and Performance
The larger your organization becomes, the more endpoints you would need to protect, so your EDR must handle more endpoints efficiently without a shift in performance. Ideally, the solution should be able to manage thousands of devices as efficiently as thousands of users, and quickly too.
9- User-Friendly Interface
The solution should also be easy to implement and administer, especially by those with no previous knowledge in cybersecurity. This makes it easier to deploy, monitor and respond to changes more effectively in an organization.
10- Vendor Reputation and Support
Last but not least are the vendor’s credentials within the marketplace or field of operation. Search for those providers that have high positive feedback of users, good services, and quality support services. Check if they provide regular updates and are quick in their replies to questions or concerns regarding the product.
Conclusion
EDR is not just the next big thing in cybersecurity terms for hype but a necessity in the next generation threat landscape. EDR has skills to detect advanced threats, investigate them, and respond to them making it possible for organizations to protect their endpoints.
However, EDR is not a technique that can be implemented once and forgotten about immediately. It needs adoption with other security technologies and measures and periodic updates to respond to emerging threats. Through the procurement of an effective EDR solution, security in endpoints can be achieved and more so the creation of an effective cybersecurity infrastructure.
When endpoints are defined as the initial first line of defense, Extended Detection and Response, EDR is the armor that you and your enterprise have against the increasing pool of threats.
If you’d like to see how the Lepide Data Security Platform can help you detect and respond to security incidents, schedule a demo with one of our engineers today.
FAQs
Q- What is the difference between EDR and traditional antivirus?
A– Traditional antivirus focuses on known threats and signature-based detection, whereas EDR provides advanced threat detection, behavioral analysis, and response capabilities for both known and unknown threats.
Q- Do small businesses need EDR?
A– Absolutely. Cyberattacks don’t discriminate based on the size of the organization. EDR offers a cost-effective way for small businesses to strengthen their endpoint security.
Q- Can EDR prevent ransomware attacks?
A– While EDR cannot prevent all attacks, it can detect and contain ransomware early in its lifecycle, limiting the damage and aiding recovery efforts.
Q- Is EDR enough for comprehensive cybersecurity?
No single solution can guarantee complete security. EDR works best when integrated with other layers of defense, such as firewalls, email security, and user training.
Q- How does EDR help with compliance?
EDR provides visibility and audit trails for endpoint activities, helping organizations meet compliance requirements for data protection and incident response.

