Last Updated on December 17, 2024 by Deepanshu Sharma

What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) can be considered as one of the key components of current cybersecurity. This simply means that it is a practice of making sure that the individuals in an organization receive the appropriate information, at the right time, from the right source, for the appropriate reasons. IAM is a practice of identifying, controlling, maintaining as well as auditing the user rights in an organization’s systems and applications.
You may think of it as a security personnel at a door to ensure no stranger is allowed in the building and a lawful visitor does not wander into a restricted area. This is especially important today when data thefts and cyber threats are becoming a norm, IAM helps to ensure the security of the information and build trust within organizations.
Why IAM Is Necessary?
Why does IAM matter? Let’s start with a scenario. Imagine a company where employees share login credentials for various applications, and no one tracks who accesses what. Sounds chaotic, right?
Without IAM, organizations leave themselves vulnerable to:
- Unauthorized Access– Hackers rejoice every time they find a system with what they consider a pathetic level of access control. When an organization has a weak IAM system, hackers can quickly take advantage of the system’s blind spots to get into the systems with restricted access to the information.
- Human Error– Even the most diligent and well-intentioned employees can make mistakes. This is very dangerous because one can easily stumble across secured documents or misuse permissions in a way that costs a lot.
- Compliance Risks– Data protection laws such as the GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS demand that companies maintain a strong handle on user access. Non-compliance leads to hefty fines and tarnishing of the companies’ reputations.
- Inefficiency– As an organization grows, it is almost impossible to manage user access and their permissions manually.
IAM gets rid of these issues because it can autonomously manage and enforce security access attributes, minimize the involvement of human input which can cause mistakes, and grant the correct level of access only to people who require it.
How Does IAM Work?
IAM operates on three primary components, i.e., identification, authentication, and authorization. Here’s how it works:
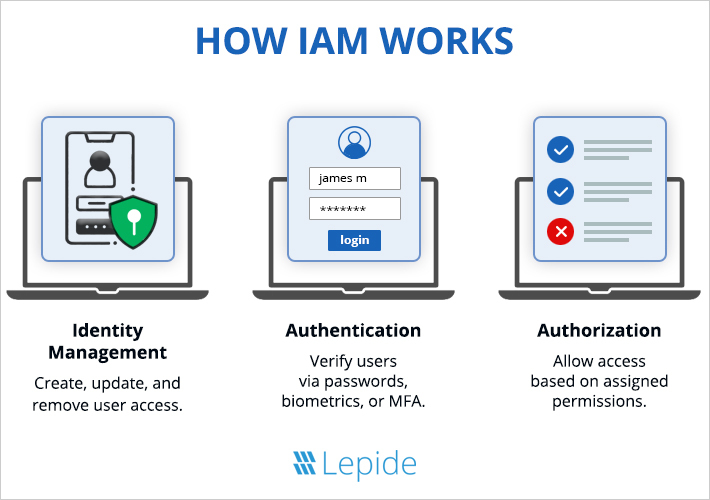
| Identity Management | Identity management in IAM involves creating, updating, and deactivating user profiles. Key tasks include account provisioning, profile management, and de-provisioning access as roles change. |
| Authentication | Authentication verifies that users are who they claim to be. This can be done through passwords, biometrics (like fingerprint scans), or multi-factor authentication (MFA). |
| Authorization | Once authenticated, the system determines what resources the user can access based on predefined permissions. |
IAM frameworks also incorporate ongoing monitoring and auditing to ensure no unusual activity goes unnoticed.
What Does IAM Do?
IAM is more than just an access management tool. Its core responsibilities extend across several domains to ensure holistic security and efficiency:
- User Provisioning and De-provisioning – IAM involves streamlining the activities of enrollment or de-enrollment involving users with various systems. For example, when employees are recruited to the organization, they are permitted the instruments required in their work. Likewise, when a person decides to leave, access is immediately denied or removed from him or her.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) – IAM also provides Single Sign-on, which allows the user to sign in and sign on to many applications without having to sign in again.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Extra layers of security are added to the identification process so that even if passwords have been hacked it is still safe.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – IAM centralizes access by roles, which makes sure that users have any level of access they need for their duties but no more.
- Monitoring and Reporting – IAM constantly monitors usage trends, reporting and raising alarms in the case of unusual usage, and creates records of usage for compliance.
IAM effectively also manages to decrease the administrative burden, and at the same time, improve the efficiency of fully automated security processes.
Typical Systems Used for Identity and Access Management
There are no readymade implemented solutions in IAM. Different organizations rely on various systems tailored to their needs:
- Cloud-based IAM Solutions– Ideally designed for organizations to use cloud infrastructure, these systems are highly compatible with SaaS solutions
- On-premise IAM Systems– Full control is another benefit that on-premise solutions offer organizations because in this case all the solutions are located within the organization’s premises and there is always an opportunity to customize the system to meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Hybrid IAM Models– In between fully cloud and fully on-site solutions, hybrid solutions have the advantages of the two models, while lacking the disadvantages of both.
- Directory Services– Products such as the Microsoft Active Directory are instrumental to IAM since they act as a centralized sign-on solution.
- Identity Federation– These systems make working across many organizations possible and give users access to external systems using their internal logins.
IAM system selection depends on the size of an organization, its type, and individual security needs that the organization possesses.
Benefits of Identity and Access Management
IAM is not just about enhancing security but is also about organizational efficiency in its broadest context, which includes trust. Let’s explore the benefits:
- Enhanced Security– IAM also plays an important function in regulating and maintaining access to resources needed, especially as it concerns the protection of data from unauthorized individuals or group.
- Improved User Experience– In the case of SSO and better access control, employees waste less of their time with login problems and instead are useful.
- Regulatory Compliance– IAM systems are known to help in meeting the regulatory requirement for data protection since they facilitate the logging of all access events and engineered protection of putting access controls into implementation.
- Cost Savings– Automation in accessing management is also beneficial in the sense that the tasks that require a lot of work from IT departments are eliminated leaving them with more work to do.
- Scalability– In organizations, as they expand, IAM becomes elastic and always can maintain high levels of security without compromising growth.
IAM is not just a powerful security solution; it is an effective business solution providing confidence and improving operations everywhere.
How Lepide Helps
Lepide Data Security Platform’s IAM solution streamlines identity and access management by offering real-time user activity monitoring to detect security threats, advanced compliance reporting with pre-built templates, and simplified role-based access control to ensure users access only what they need. Seamlessly integrating with systems like Active Directory, it provides a unified platform tailored to the security and compliance needs of organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises.
Conclusion
IAM is not a luxury in the current Digital Environment. With cyber threats changing as they are, the application of robust IAM solutions is as important as ever. In either case, whether it’s for protecting data, compliance, or better operational processes; IAM is the first step to a safer tomorrow.
Through Lepide and similar solutions, identity and access management doesn’t need to be complicated. It simply means that whenever one takes up any decision, it is about preparing for the future.
FAQs
Q- What is the primary purpose of IAM?
A- IAM ensures that only authorized individuals have access to specific resources, safeguarding sensitive information and improving operational efficiency.
Q- What are some common IAM tools?
A- Popular IAM tools include Microsoft Azure AD, Okta, and SailPoint. These tools provide features like SSO, MFA, and access monitoring.
Q- Is IAM only for large organizations?
A- No, IAM is beneficial for businesses of all sizes. Small and medium-sized enterprises can also leverage IAM to enhance security and streamline operations.
Q- How does IAM support compliance?
A- IAM simplifies compliance by enforcing access control policies and generating detailed audit logs, ensuring organizations meet regulatory requirements.
Q- What makes Lepide’s IAM solution unique?
A- Lepide combines advanced monitoring, seamless integration, and compliance-ready reporting to deliver a robust and user-friendly IAM solution.


 Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration
Group Policy Examples and Settings for Effective Administration 15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them
15 Most Common Types of Cyber Attack and How to Prevent Them Why AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
Why AD Account Keeps Getting Locked Out Frequently and How to Resolve It
